What is UX Design?
Understanding the significance of Pearson is revealed in
In the contemporary virtual age, user enjoyment (UX) design plays a crucial function in growing successful and attractive products and services. Whether you’re surfing a website, using cell software, or interacting with a digital interface, the excellence of the user experience can substantially impact your satisfaction and a basic belief in the emblem. This newsletter will delve into the arena of UX design, explaining its definition, concepts, and the cost it brings to each customer and corporation.
1. Introduction to UX Design
Person revels in (UX) design refers to the technique of improving user pleasure via enhancing the usability, accessibility, and delight supplied while interacting with a product or service. It encompasses various aspects such as visual design, information architecture, interaction design, and usability. UX designers attempt to create seamless and exciting experiences that meet the needs and expectancies of the target market.
Read more: A UX Designer: Creating Seamless User Experiences-UX Design
2. Key Principles of UX Design
To create powerful UX designs, designers follow numerous key principles:
User-centered layout: placing the person at the center of the design process and information on their desires, behaviors, and alternatives.
Simplicity: Striving for simplicity and minimizing complexity to facilitate ease of use.
Consistency: Maintaining consistency in design elements and interactions across the product to provide a familiar and intuitive experience.
Clarity: Ensuring clear and concise communication through well-structured content, visual hierarchy, and intuitive navigation.
Accessibility: Designing with inclusivity in mind, ensuring that the product can be used by people of all abilities.

3. The Process of UX Design
The UX design process typically involves the following stages:
Research: Conduct user research to understand the target audience, their needs, and their pain points.
Information Architecture: Organizing and structuring information in a way that is logical and easy to navigate.
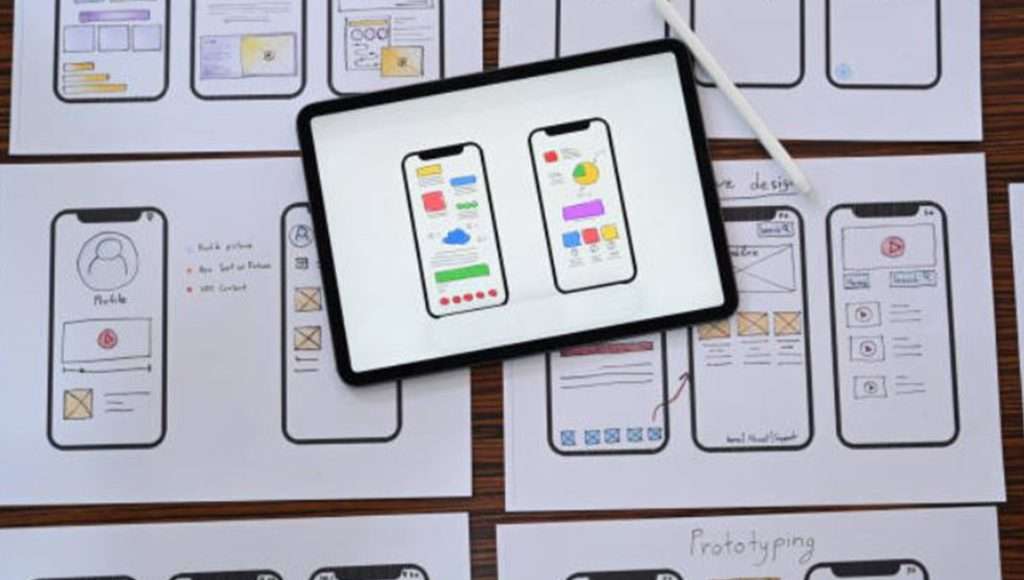
Wireframing and Prototyping: Creating low-fidelity wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the user interface and interactions.
Visual Design: Enhancing the aesthetics of the product while ensuring visual consistency and alignment with the brand.
Testing and Iteration: Conduct usability tests and gather feedback to identify areas for improvement and iteratively refine the design.
Implementation: Collaborating with developers to ensure the design is implemented accurately and according to specifications.
4. The Benefits of UX Design
Effective UX design offers numerous benefits for both users and businesses, including:
Enhanced User Satisfaction: By focusing on user needs and preferences, UX design creates enjoyable and satisfying experiences.
Elevated user Engagement: Intuitive and nicely designed interfaces encourage users to engage extra deeply with the services or products.
Improved Conversion Rates: A seamless and user-friendly experience can lead to higher conversion rates and business growth.
4. The Benefits of UX Design (continued)
Reduced Development Costs: Early identification of usability issues through UX design can save costs by addressing them in the design phase rather than during development or post-launch.
Competitive Advantage: Providing exceptional user experiences sets businesses apart from competitors and fosters customer loyalty.
Increased Customer Retention: Positive experiences lead to repeat visits and increased customer loyalty.
Positive Brand Perception: A well-designed and user-friendly product or service reflects positively on the brand and its reputation.
5. Understanding User Research
User research is a critical component of UX design. It involves gathering insights about users, their behaviors, motivations, and needs. Strategies such as surveys, interviews, and user trying out are employed to gain deep expertise of the target market. The data collected through user research guide design decisions and helps create user-centric solutions.

6. Importance of User Testing
User testing involves observing and collecting feedback from users as they interact with a prototype or a live product. It helps identify usability issues, pain points, and areas for improvement. By involving real users in the testing process, UX designers can refine the design and ensure a seamless user experience.
7. UX Design vs. UI Design
At the same time as UX design and UI layout are regularly used interchangeably, they constitute exclusive components of the design process. UX layout specializes in the general user experience, consisting of consumer research, records structure, and interplay design. UI design, alternatively, deals with the visible elements and aesthetics of the interface, which includes hues, typography, and design. Both UX and UI design are essential for creating outstanding user experiences.
8. The Role of UX Designers
UX designers play a crucial role in creating user-centered designs. They collaborate with stakeholders, conduct research, define user personas, create wireframes and prototypes, and conduct usability tests. They paint intently with developers and UI designers to make certain the very last product aligns with the person’s wishes and enterprise goals.
9. UX Design Tools and Technologies
Various tools and technologies assist UX designers in their work. These include wireframing and prototyping tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Fatma, usability testing platforms like User Testing, analytics tools like Google Analytics, and collaboration platforms like IN Vision.
10. Incorporating Accessibility in UX Design
Accessibility is a crucial issue of UX layout, ensuring that products and services may be accessed and utilized by people with disabilities. Designers need to consider factors such as screen readers, color contrast, keyboard navigation, and alternative text for images to ensure inclusivity.
11. Mobile UX Design Considerations
With the widespread use of mobile devices, mobile UX design has gained immense significance. Designers must create responsive and mobile-friendly interfaces, optimize loading times, and consider mobile-specific interactions such as touch gestures and screen real estate limitations.
12. Website UX Design Best Practices
When designing websites, UX designers follow best practices such as creating clear and intuitive navigation, optimizing page loading speed, utilizing whitespace effectively, providing informative and engaging content, and ensuring mobile responsiveness.
13. UX Design for E-Commerce
UX layout plays a crucial role in e-trade, where the user revel in immediately affects conversion prices and income. Seamless product browsing, intuitive checkout processes, personalized recommendations, and easy return processes are some key aspects of e-commerce UX design.
14. Measuring UX Success
To measure the success of UX design efforts, designers analyze key metrics such as user engagement, conversion rates, task completion rates, bounce rates, and customer satisfaction surveys. These metrics provide insights into the effectiveness of the design and identify areas for improvement.

15. Conclusion
In conclusion, UX design performs a crucial position in growing terrific person stories that power patron pleasure and enterprise achievement. By specializing in user-focused principles, engaging in thorough studies, and following a nicely defined design procedure, UX designers can create intuitive, fun, and attractive products and services.
A well-executed UX design enhances user satisfaction, increases user engagement, and fosters positive brand perception. It leads to higher conversion rates, improved customer retention, and a competitive advantage in the market. By incorporating accessibility considerations, adapting to mobile platforms, and following best practices, UX designers can create outstanding digital experiences.
To achieve success in UX design, continuous testing, iteration, and measurement of key metrics are essential. By listening to user feedback, staying updated with industry trends, and utilizing the right tools and technologies, UX designers can deliver meaningful and impactful designs.
Inside the ever-evolving virtual panorama, prioritizing UX layout is essential for corporations looking to distinguish themselves and construct lasting relationships with their customers. By using setting users at the center of the design technique, agencies can create stories that delight, encourage, and meet the ever-growing expectancies of their audience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does UX design vary from UI design?
A: UX design makes a specialty of the general person revel in, such as research, records structure, and interplay design, at the same time as UI design offers the visual aspects and aesthetics of the interface.
Q: What tools are commonly used in UX design?
A: Popular tools in UX design include Sketch, Adobe XD, Figma, UserTesting, Google Analytics, and InVision.
Q: Why is accessibility important in UX design?
A: Accessibility guarantees that services and products can be accessed and utilized by people with disabilities, selling inclusivity and getting admission to all.
Q: How can UX design benefit e-commerce websites?
A: UX design improves the person’s level in e-trade websites, leading to better conversion rates, multiplied sales, and improved purchaser delight.
Q: How can the success of UX design be measured?
A: Key metrics inclusive of user engagement, conversion prices, assignment completion charges, bounce costs, and client pride surveys are used to measure the fulfillment of UX design efforts.
Incorporating UX design principles and practices can transform the way businesses engage with their users, ensuring memorable and impactful experiences that drive growth and success.